Introduction to AWS Athena Amazon Athena is an interactive query service that makes it easy to analyze data directly in Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3) using standard SQL.
Features:
- Athena is serverless. So there is no infrastructure to set up or manage, and you pay only for the queries you run.
- It scales automatically and also executes queries in parallel.
- Results are fast even with large data sets and complex queries.
- Athena helps you to analyze unstructured, semi-structured, and structured data stored in amazon s3. eg: Apache Web Logs, CSV, TSV, Text file with custom delimiters, JSON, etc.
- We can access Athena using AWS management console, JDBC or ODBC connection, Athena API, Athena CLI.
- It is Cost-effective – We pay only for S3 which is quite cheap, and externally we pay per query. Per query cost – 5 dollars per Terabyte scan for S3.
Presto (SQL on anything): Athena uses Presto as a managed service. Presto is an in-memory distributed SQL engine, which came out of Facebook. It reads data from anywhere and actually processes data from where it lives; hence it can be connected to a variety of connectors including HDFS, S3, MongoDB, MySQL, Postgres, Redshift, SQL Server. It has the power to handle hundreds of concurrent queries on a single cluster. That means we don’t have to maintain complex clusters.
So it supports commands like creating a table, nested queries, multiple joins. We can also partition the data based on any column, not just date and time, but can also make a combination of several columns. It uses Hive QL for DDL, and Presto while querying the data.\
Querying data from S3-Bucket using Athena:
- We took sample data set from https://www.kaggle.com/shivamb/netflix-shows which is of CSV format and uploaded it to s3://kartheek-athena/ which is test bucket.

- On global search type Athena and select Athena-Query data in S3 using SQL.

- Now you will see the following screen, we need to click on Connect Data Source.

- Here we need to choose where our data is located, I will select Query data in Amazon S3 and will click on the Next button.

- Now we need to specify connection details i.e Athena will connect to your data stored in Amazon S3 and use AWS Glue Data Catalog to store metadata, such as table and column names.
- This can be done in two ways i.e setup a crawler in AWS Glue to retrieve schema information automatically and another way is to add a table and enter schema information manually.

- This can be done in two ways i.e setup a crawler in AWS Glue to retrieve schema information automatically and another way is to add a table and enter schema information manually.
- Select the second option and click on the continue to add table button.

- Here we need to specify the database name, table name, and location of the input data set and click on the next button.
- Now we need to select data format i.e CSV and click on the next button.

- Add columns for the table, in order to add multiple columns at a time, we can click on the bulk add columns .

- Define schema for the table and click on the next button.
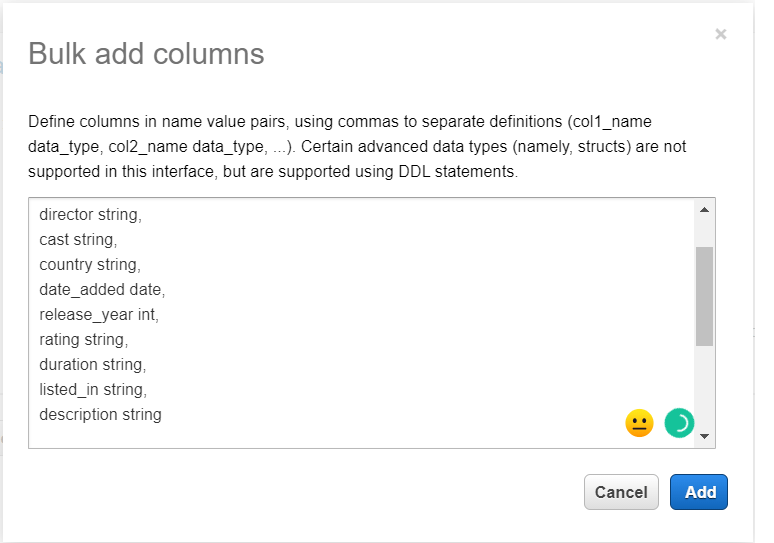
- Partitions are the way to group specific information and it is option and we can proceed further by clicking on the Create table button.

- It will redirects us to the Query Editor screen

- Now we can start querying data by writing simple queries.
SELECT COUNT(*) AS TotalRows FROM "athenatest"."netflix_info"
Result

- Query2
SELECT Title,
Director,
Country,
Rating
FROM "athenatest"."netflix_info"
WHERE Type = 'Movie'
AND COUNTRY != ''
ORDER BY COUNTRY ASC;
Result

By this way we can make use of SQL to Query S3 files with AWS Athena
